
Recently, a medical research team formed by Shanghai Fourth People's Hospital, Tongji University, and Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, made a significant breakthrough in the study of the mechanism of lung metastasis related to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The relevant findings were published in "Cancer Letters"[1] with an impact factor of 9.756. This discovery suggests that circulating tumor cells (ICAM-1+CCSCs) can serve as a novel biomarker for assessing the risk of lung metastasis in patients with HCC.
So, how was the precise quantification of the expression levels of circular RNA (circ-CDYL) in ICAM-1+CCSCs achieved?
The researchers addressed this challenge using the Digital PCR technology provided by Turtle Technology: dividing circulating tumor cells (CTCs) into two groups, one with high ICAM-1 expression (i.e., circulating cancer stem cells or CCSCs) and the other with low ICAM-1 expression (i.e., ICAM-1-CTCs). The analysis results showed that the circ-CDYL levels in CCSCs were significantly higher than those in ICAM-1-CTCs among HCC patients. Simultaneously, this study provides insights into the biological processes of other solid tumors, suggesting that a low oxygen microenvironment may play a potentially crucial role in regulating tumor heterogeneity and organ-specific metastasis.
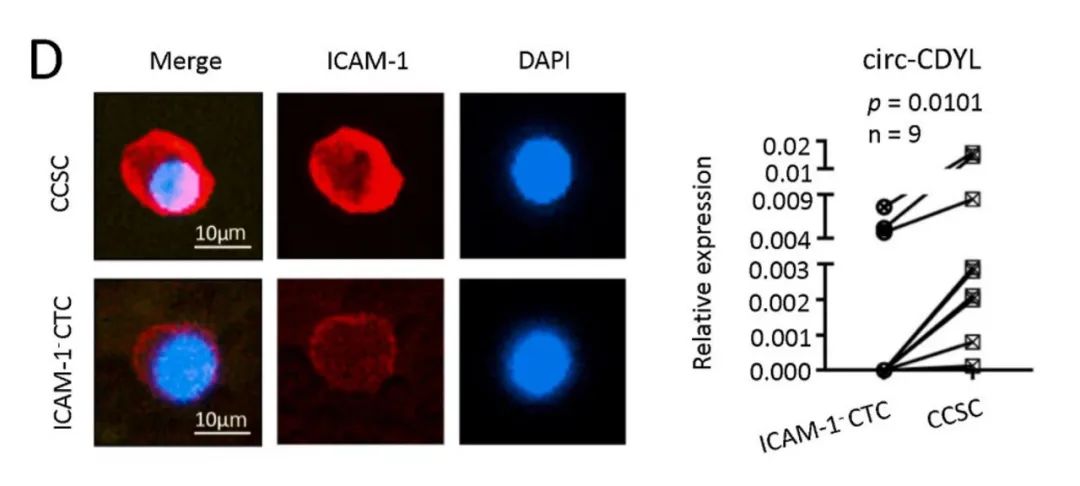
Left panel, fluorescent images of ICAM-1+ (CCSCs) and ICAM-1- CTCs. Right panel, circ-CDYL was analyzed in CCSCs versus ICAM-1- CTCs in 9 HCC patients by digital PCR.
This research provides a new approach for the detection of tumor-related circular RNA, offering important experimental and technical support for tumor diagnosis and treatment. It reveals a crucial link in the liver cancer lung metastasis process, laying a theoretical foundation for targeted therapy. As circular RNA plays a significant role in tumor progression and Digital PCR technology provides highly sensitive and accurate detection results, it contributes to a better understanding of the biological characteristics and pathophysiological processes of tumors. This is of great significance for the diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and monitoring of tumors.
In conclusion, Turtle Technology's propietory Digital PCR technology and detection platform make it possible for researchers to accurately detect extremely low-abundance circ-CDYL in samples from HCC patients. We look forward to the important role Digital PCR technology will play in early screening and targeted treatment monitoring for various diseases.
If you are conducting research in a related field, feel free to contact Turtle Technology for technical exchanges and collaboration. We are committed to providing technical support and jointly promoting the multiple transformations of Digital PCR technology in research and clinical applications.
About Turtle Technology
Turtle Technology is committed to leading the life sciences and molecular diagnostics into the digital era. Having been approved as the National Demonstration Center for Genetic Testing Technology and obtaining the first Digital PCR Metrological Evaluation Certificate, we have introduced a variety of digital PCR systems. This marks a comprehensive technological innovation across the entire industrial chain, including genetic testing instruments, chip consumables, Ultra-Multiplex technology, and ultra-high specificity polymerase.
Reference:
[1] R. Kong, et al. Hypoxia-induced circ-CDYL-EEF1A2 transcriptional complex drives lung metastasis of cancer stem cells from hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letters, 578 (2023) 216442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216442.